
While HBV is not directly cytopathic, the host-mediated response to infected hepatocytes is thought to mediate chronic liver injury. Chronic HBV infection is characterized by the persistent presence of HBsAg for at least 6 months. The proportion of patients progressing to chronic infection is much higher in neonates (up to 90 percent) compared with 1 to 5 percent in adults and intermediate values in young children. Serologic testing is characterized by positive hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) and IgM antibody to hepatitis B core antigen (IgM anti-HBc). Constitutional symptoms, anorexia, nausea, jaundice, and right upper quadrant discomfort can occur during the prodromal phase, and typically disappear after 1-3 months. HBV infection in children has a variable course ranging from asymptomatic infection to fulminant hepatitis, with an incubation period of one to four months.

The incidence of acute HBV infection among US children and adolescents declined dramatically during the era of universal childhood vaccination, from 3.03 reported pediatric cases per 100,000 population in 1990 to 0.34 per 100,000 in 2002.Since then, surveillance data from the Center for Disease Control (CDC) from 2011 to 2020 has continued to demonstrate low acute HBV infection rates (0.0 cases per 100,000) among children age 0-19 years.
#Most common hep b transmission in adolescent update#
Update on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of chronic hepatitis B: AASLD 2018 hepatitis B guidance. Perinatal transmission in non-endemic countries, including the United States, occurs most commonly in children of HBV-infected mothers who do not receive appropriate HBV immunoprophylaxis at birth. In countries where HBV is endemic, HBV infection occurs mainly during infancy and early childhood with perinatal transmission accounting for up to 90% of all chronic HBV infections. Worldwide, HBV infection prevalence is highest in the Asia, Africa, Southern Europe, and Latin America, where hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) positive rates in the general population range from 2 to 20%. Rates of HBV infection vary substantially by geographic region. Approximately 1 million people per year die from hepatitis B-related complications worldwide. Hepatitis B is the 2 nd most common carcinogen worldwide after tobacco.
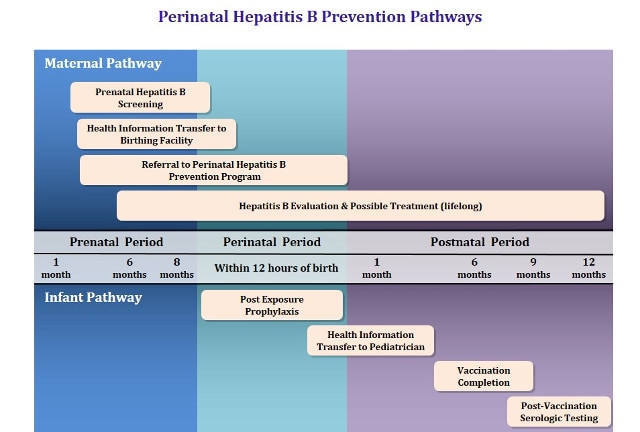
Approximately 90% of those with chronic infection were infected perinatally, primarily in Asia ( 75% of chronic cases).Those with chronic infection are at highest risk of developing complications of the infection, including liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Although the virus can infect people of any age, those who are infected perinatally or as children are at greatest risk for chronic infection. Despite availability of an effective vaccine, hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection remains a worldwide public health issue with approximately 1.5 million new infections per year and an estimated 292 million chronic carriers.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
